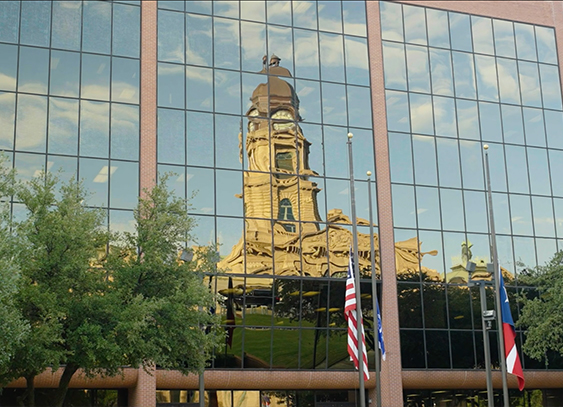
Rear-End Collision Injuries and How You Can Recover
In just a split second, a rear-end accident can alter the course of your entire life. That’s because recovering from a rear-end crash doesn’t just mean going through the recovery process to heal your rear-end collision injuries. It also involves recuperating financially. Without monetary support, you could be in dire straits for the rest of […]
Read more